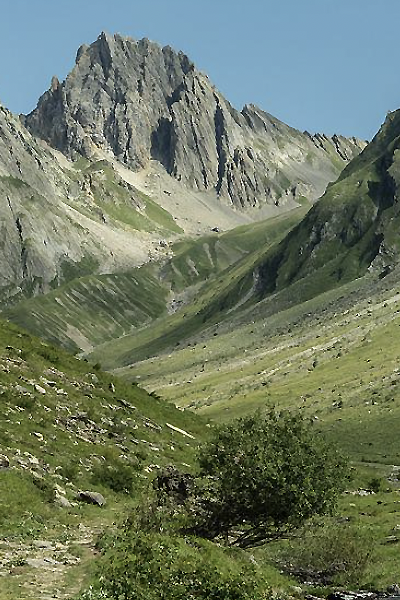
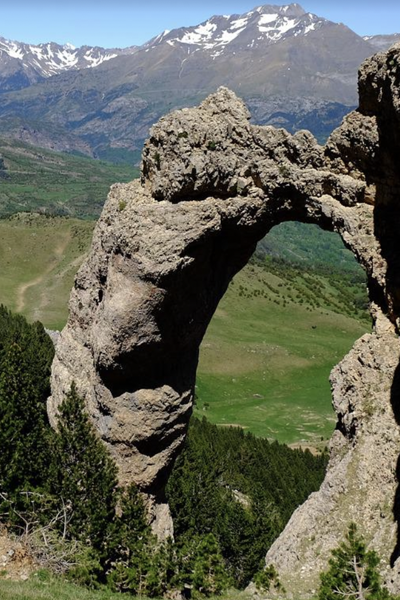
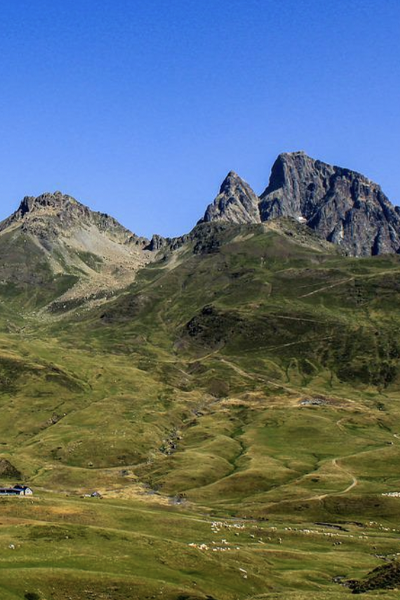
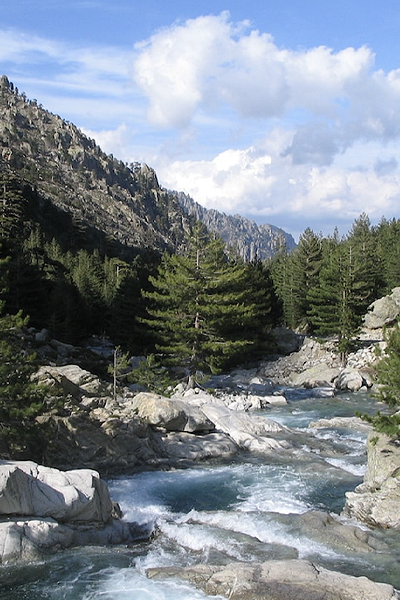
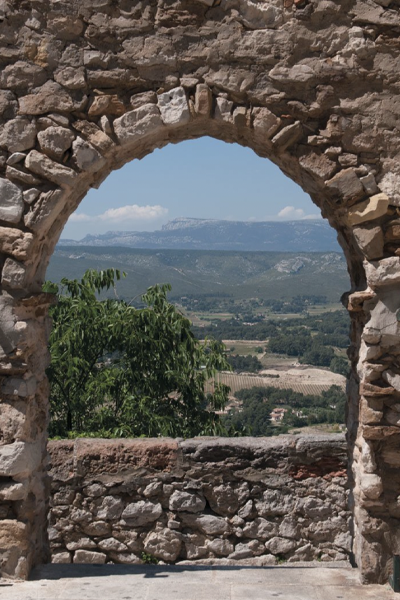
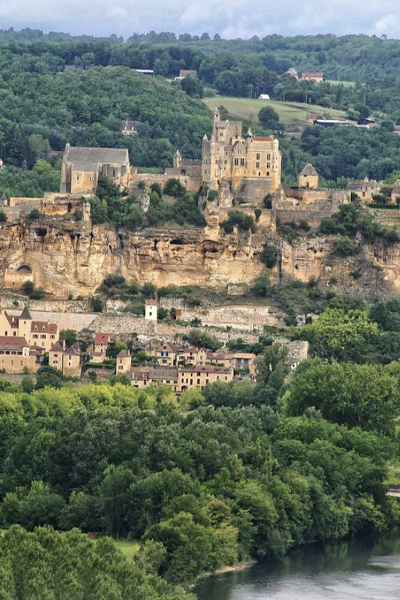
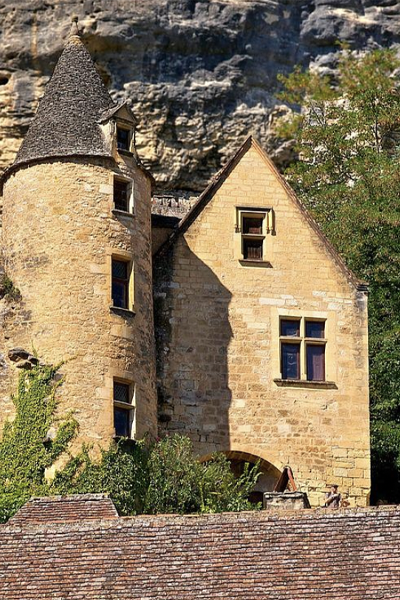
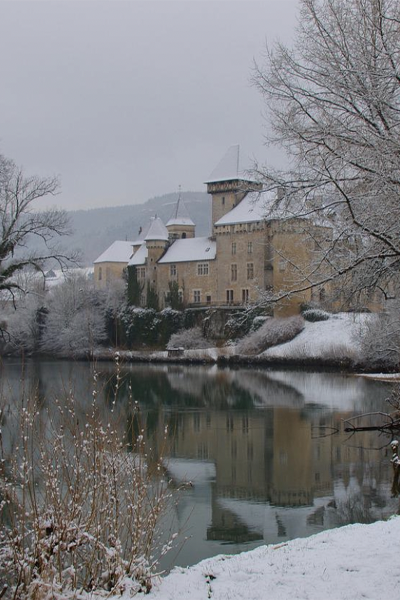
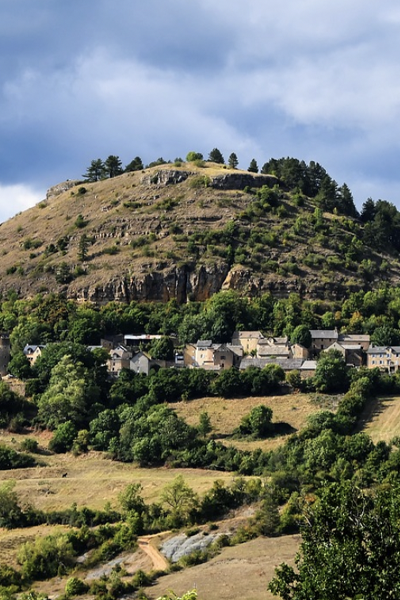
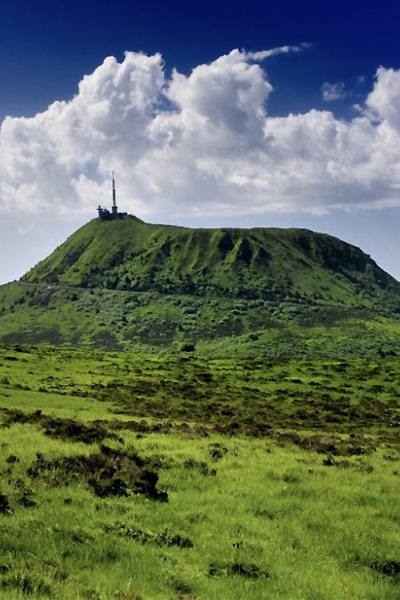
Le Mas station is situated in the commune of Farges en Dordogne at the top of a hill composed of Cretaceous calcareous rock bordered by a grassland area planted with truffle-bearing oaks. Its climate is temperate, intermediate between oceanic and semi-continental. The summers are hot, but not systematically dry, the winters being humid and relatively mild. The mean annual temperature during the period 1971-2000 was 12.2°C, increasing during the subsequent decades. The mean annual rainfall is close to 950 mm, but varies widely from year to year.
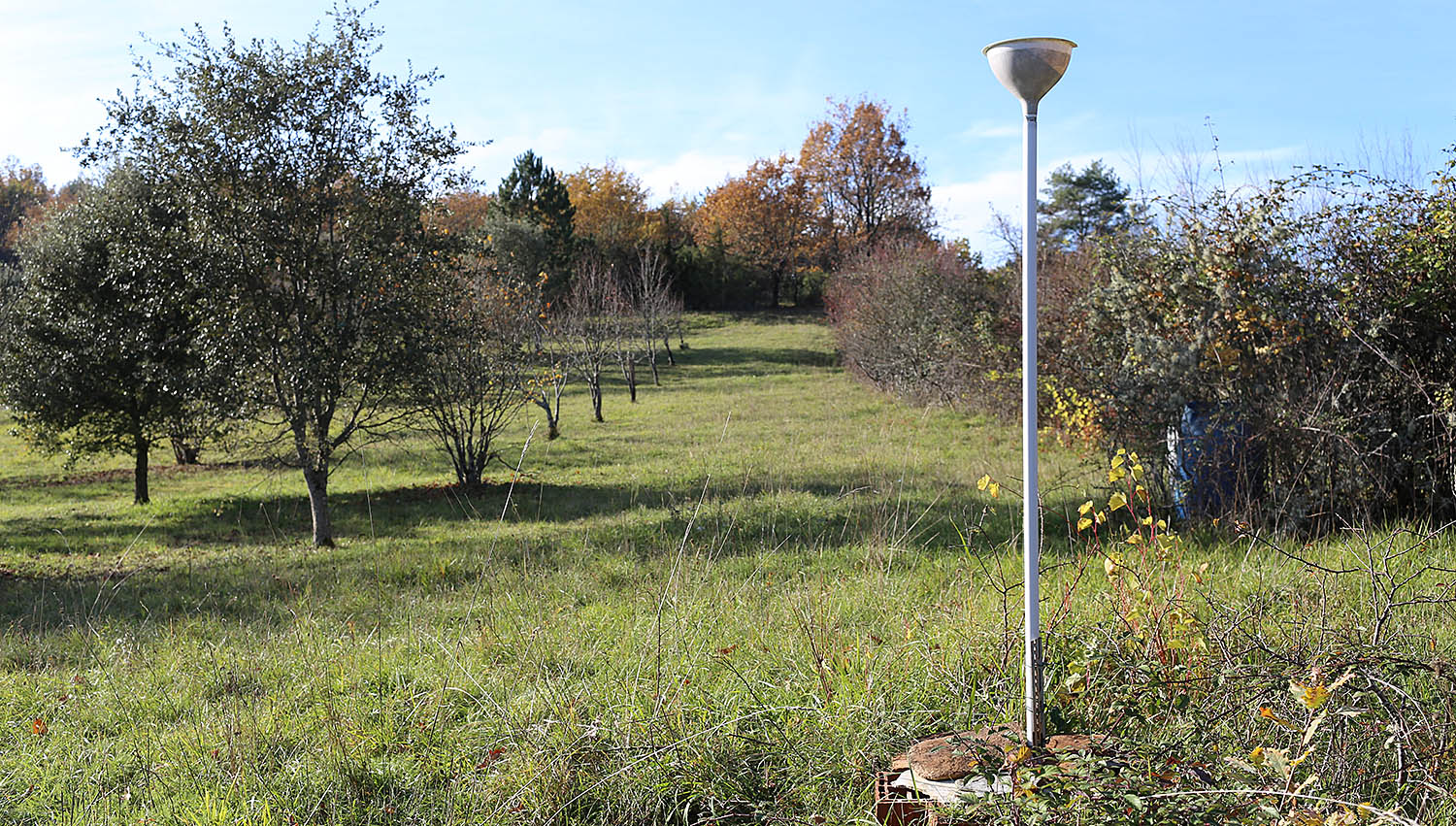

A long isotopic series in a temperate oceanic and karstic context
The Le Mas station was established in 1998 close to several caves containing stalagmites used for paleoclimatic reconstitutions. The objective of this research is to compare the isotopic signals of rainwater and the subterranean water supplying speleothems. Owing to its location, quite close to the Villars station (30 km away) and at the same altitude, the Le Mas station can check measurement consistency and analyse subtle differences in isotopic signals between the two sites, the Villars station being exposed to a slightly more continental climate. As at the Villars station, comparison of variations in the isotopic characteristics of rainwater between different seasons and different years with those of water sources, using retro-trajectory models demonstrated the non-negligible impact of this factor on isotopic composition.

Presentation of the Le Mas station
The Le Mas station has been taking samples of precipitation once a month since 2019. During the period 1996-2019, samples were taken every 1 to 3 months.
Up to 2007, meteorological data were provided by the Météo France station located in Montignac (7.6 km SSW from the Le Mas station). From 2007 to 2018, meteorological data were generated by a station installed at a distance of 25 m from the associated collector. From 2019 onwards, reference meteorological data have been supplied by the Chourgnac station (situated 15 km NW from the Le Mas station).
Latitude
Longitude
Altitude